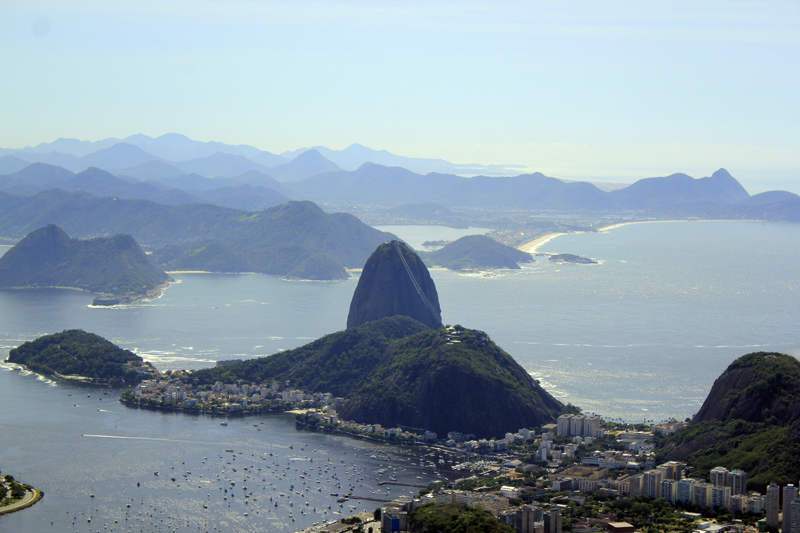
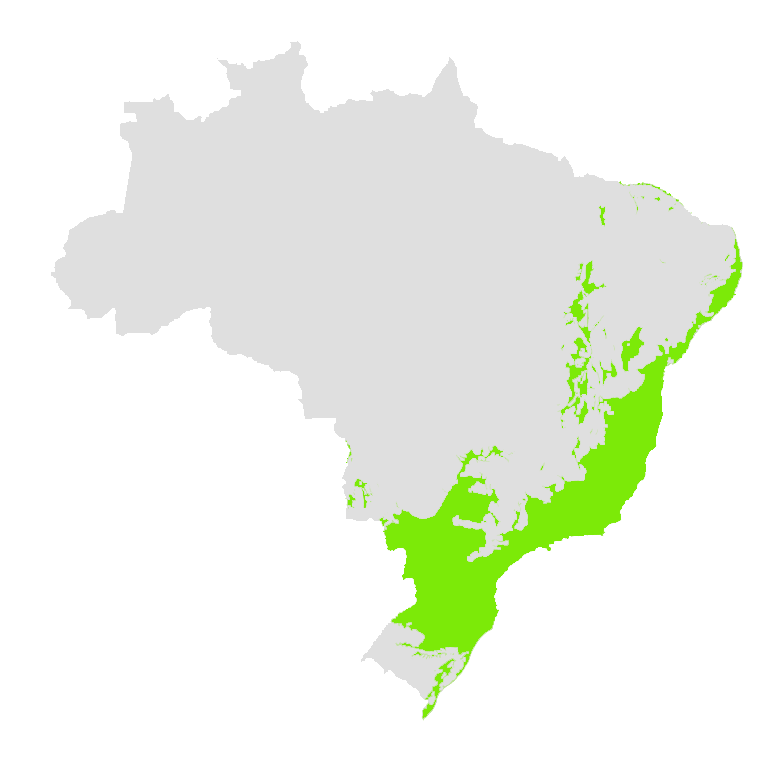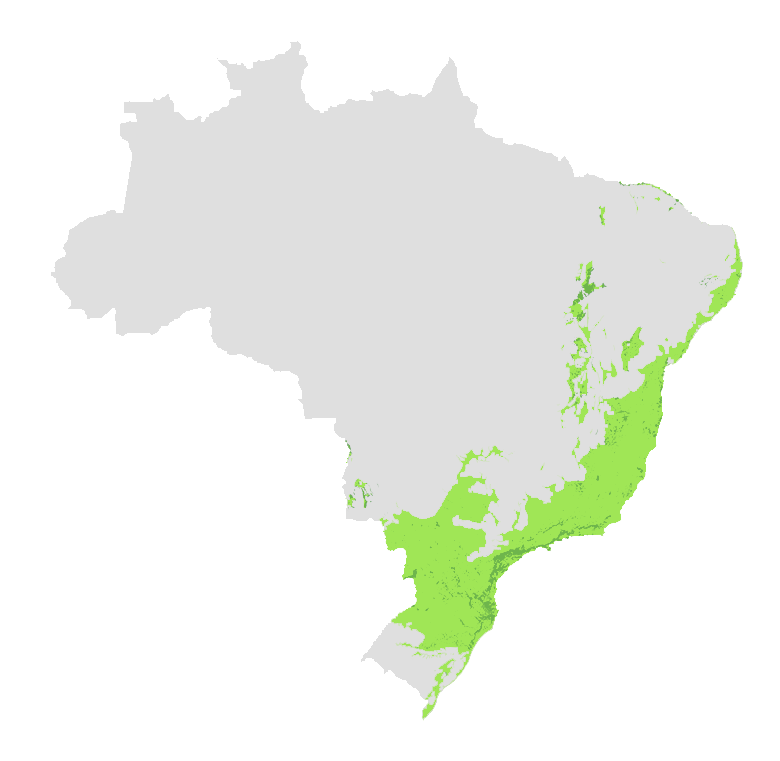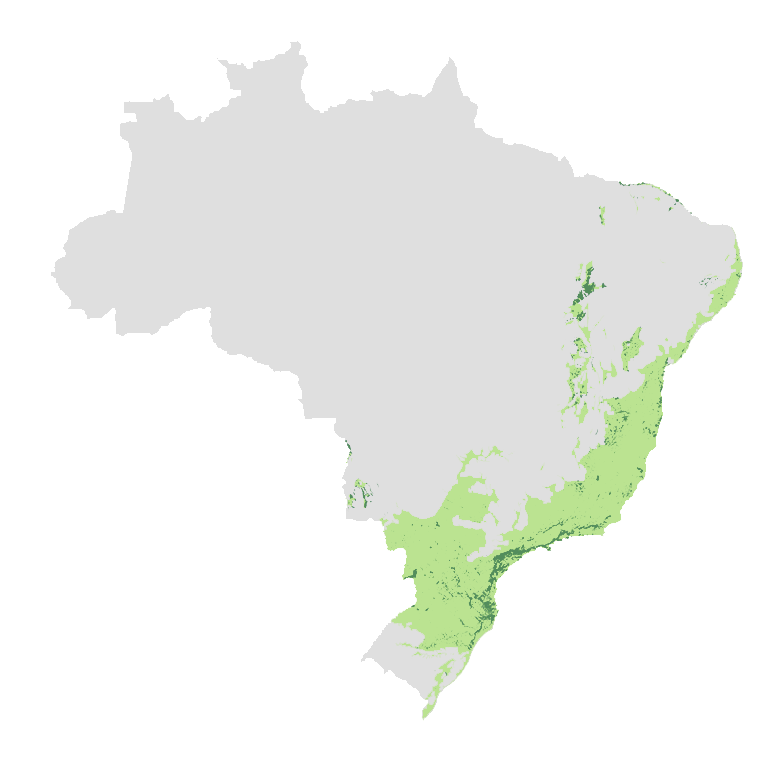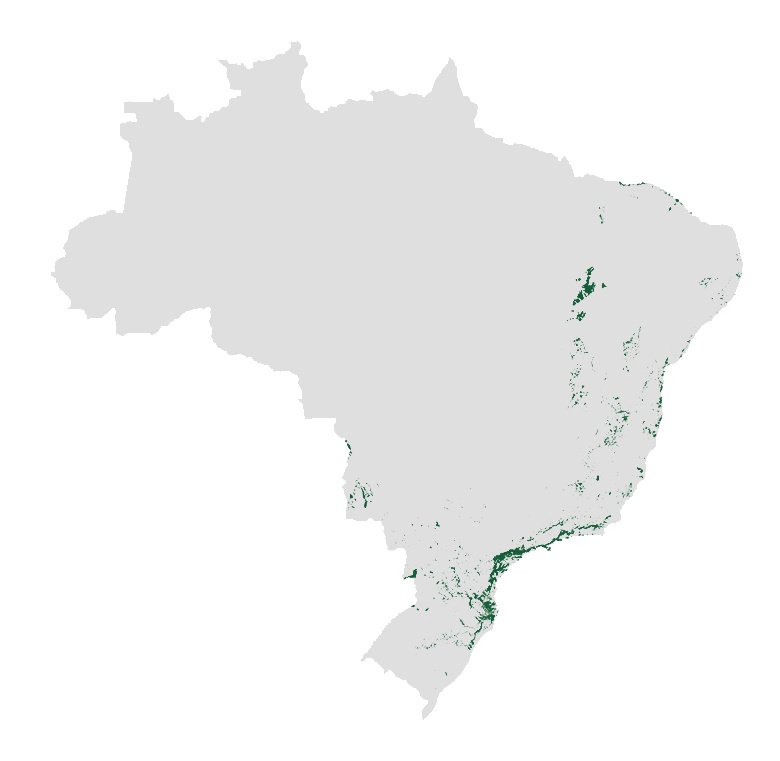
The Atlantic Forest is a
megadiverse tropical forest, among the
top 5 biodiversity conservation hotspots in the world. More than 90% of the biome is inside Brazil, but it is also present in Argentina and Paraguay.
It is one of the six biomes of Brazil, which also include: Amazon, Caatinga, Cerrado, Pampa and Pantanal.
It occupies 15% of the Brazilian territory, being present in 3,429 municipalities of 17 States of the country. Its original area was 3.6 times larger than Germany.
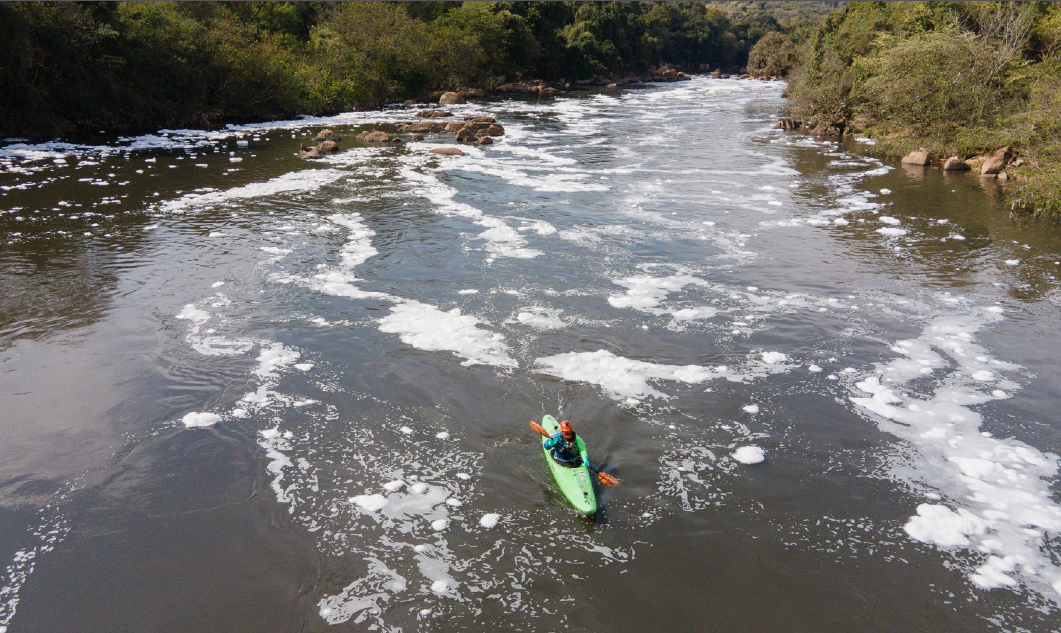
The Atlantic Forest covers nine of the 12 Brazilian hydrographic regions and many of its rivers have problems of water quantity and quality, although they supply most of the national population and industry.
Its home to 70% of the Brazilian population (145 million
people) and 80% of the national GPD.
The Atlantic Forest and the Amazon are the Brazilian biomes with predominance of moist tropical forests. The Amazon occurs mostly in the Basin of the Amazon river while the Atlantic Forest is mainly present in the coastal region and Southern inland regions of Brazil.
It is the main agriculture region of Brazil and produces most of the staple crops and food consumed internally. The Atlantic Forest is also responsible for the pollination of important crops.
Besides its 500 years supplying Europe with goods, today it is connected to the world through the trade of commodities like pulp, sugar, coffee and orange juice. Significant part is certified by green labels like FSC and Rainforest Alliance.